Cannabinolic acid (CBNA) is a delicate molecule that is closely related and rapidly breaks down into CBN. With such little direct research into CBNA, its specific pharmacological profile is largely unknown. Therefore, CBNA may be reasonably assumed to act like the more stable and nonintoxicating cannabinol (CBN).
A 2021 study on CBNA and THC showed its potential for pain relief in mice. Researchers also discussed CBNA’s potential anti-nausea, antianxiety, and antidepressant activity similar to cannabidiol (CBD).
Since CBNA effectively breaks down into CBN, they likely share potential benefits including anti-inflammatory, anti-glaucoma, anti-allergy, antibacterial, and anti-emetic. Side effects may include increased appetite and sleepiness.
What Is CBNA?
CBNA is a fleeting compound created in trace amounts by storing and aging cannabis. It is not found in fresh hemp because no enzyme makes it, and it’s unstable. Cannabis plants have 0.1–1.6% CBN, with even less CBNA than CBN found only in aged samples.
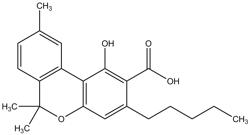
CBNA is considered an artifact, or byproduct, of natural cannabis breakdown (oxidation). Specifically, THCA that is exposed to light, UV rays, heat, air, or time becomes CBNA.
However, discoveries of ancient cannabis rituals reveal that CBN is the ultimate, primary degradation product of many cannabinoids, including CBNA, THCA, and THC.
CBNA vs. THC: Key Differences
- CBNA is non-intoxicating, while THC will cause a high
- THC is a greater sedative than CBN, which may not be as sedating as marketed. There may be some sleep-inducing effects with CBN, likely best when combined.
CBNA vs. CBD: Key Differences
- Both have anti-inflammatory properties, but CBN may have an edge in allergic airway disease
- CBN, but not CBD, may be used in glaucoma to prevent inflammation that results in elevated eye pressure (IOP)
- CBD may increase pain-relieving effects of CBN in a 1:1 formulation
What Are the Benefits and Effects of CBNA?
There are only a couple of studies directly examining the biological effects of CBNA. In a 2021 publication, CBNA reduced mechanical and heat-induced pain in mice. THC also did so separately, but both exhibited lessening effects over 4–5 days of chronic dosing.
Pharmaceutical companies are currently investigating the anti-cancer effects of CBNA and CBCA. Results show similar cytotoxicity on human colon cancer cells as their neutral, or non-acidic forms (e.g., CBN, CBC) do in test tubes.
Computer docking models in 2022 predict CBNA may restrict viral entry of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. However, no in vivo or in vitro studies have been done yet.
Without further direct studies on CBNA, we can only approximate its activity as comparable to CBN which is its more commonly encountered and stable form. These potential benefits may include:
- Pain relief: CBN may mitigate symptoms of myofascial pain disorders like TMDs and fibromyalgia. CBD may potentiate these in a 1:1 ratio.
- Anti-inflammatory: Antioxidant activity may decrease cell damage in a culture model of Huntington’s
- Anti-allergic effects: Decreases pro-inflammatory molecules and reduces allergen mucus production in mice; may help with allergic airway diseases like asthma, etc.
- Antibacterial: Including MRSA and multiple resistant bacteria; may help staph infections
- Alleviating Epidermolysis Bullosa: Phase 1 and 2 CBN cream trials show promising results with no serious adverse effects; Phase 2 trials to clinically evaluate anti-itching effects show it’s well-tolerated but falls short of significant results over placebo
- Neuroprotective and anti-glaucoma agent: CBN may reduce IOP via anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective pathways; Phase 1–2 trials are being initiated
What Are the Side Effects of CBNA?
Lack of the existence of any clinical studies on CBNA limits our knowledge of its side effects. However, CBN’s side effects also likely apply here as well, including:
- Sleepiness: CBN is often marketed as “the sleepy cannabinoid in old weed” with ineffective dosing often suggested by manufacturers. CBN’s sleep induction is unclear, but it could be additive with THC and viewed as either a side effect or benefit, depending on the consumer.
- Increased appetite: Like sleep promotion, induction of appetite can be viewed as a positive or adverse effect. However, CBN’s lack of psychotropic effects make it more tolerable to a wider audience
We should also note the lack of side effects that come with other cannabinoids like THC: no intoxication (high), or alterations of heart conduction, rate, blood pressure, or body temperature.
How Much CBNA Should You Take?
CBN manufacturers will often suggest doses of just 5 mg or less at a time. In my experience, that is not enough to induce sleep effects in people with insomnia or even elderly patients.
Without clear research, CBN or CBNA dosing should follow the usual dosing for non-intoxicating cannabinoids, starting with at least 5–10 mg in your first dose. Staying close to a 1:1 ratio with your other cannabinoids may help increase their effectiveness, like THC and CBD mentioned above.
Following up with your healthcare provider and a cannabis coach like me can help you adjust and optimize your doses, cannabinoids, and terpene selection further.
Will CBNA Get You High?
No, CBNA will not cause a high. Although CBNA isn’t formally studied in humans, there is enough supporting data for scientists to universally recognize it is non-intoxicating.
CBN alone will also not cause a high, unless your products are contaminated with more than 0.3% THC. CBN may increase the high and sleepiness of THC, but not alter THC’s other side effects.
Will CBNA Show Up on a Drug Test?

CBNA will not cause a positive drug test result unless it is in a full-spectrum formulation with THC present.
Of note, drug testing labs are always looking for new ways to enhance testing and differentiate between pharmaceutical and herbal THC use. Minor cannabinoids like CBN are now biotargets in such testing; avoiding any concurrent THC consumption is best if this is a concern.
Conclusion
CBNA remains elusive but promising. Even as pharmaceutical companies look for new ways to artificially manufacture and use it.
Related Cannabinoids
References (20)
- Biomedican. (2023). Cannabinol: What is CBN, benefits and effects | CBNA synthesis by Biomedican. BIOMEDICAN. https://biomedican.com/cbn-cbna/
- Biomedican. CBN Research: Health and medical research of Cannabinol and CBNA. (2023). BIOMEDICAN. https://biomedican.com/cbn-and-cbna-research/
- InMed Pharmaceuticals. (2023). Cannabinol CBN – Rare Cannabinoid Under Development for Glaucoma. InMed Pharmaceuticals. https://www.inmedpharma.com/pharmaceutical/inm-088-for-glaucoma/
- InMed Pharmaceuticals. (2023, June 22). InMed Pharmaceuticals Inc. Announces Results from a Phase 2 Clinical Trial in Epidermolysis Bullosa. InMed Pharmaceuticals. https://www.inmedpharma.com/news_release/inmed-pharmaceuticals-inc-announces-results-from-a-phase-2-clinical-trial-in-epidermolysis-bullosa/
- Chen, C., Liang, H., Deng, Y., Yang, X., Li, X., & Hou, C. (2022). Analysis and Identification of Bioactive Compounds of Cannabinoids in Silico for Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Biomolecules, 12(12), 1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12121729
- Maioli, C., Mattoteia, D., Amin, H. I. M., Minassi, A., & Caprioglio, D. (2022). Cannabinol: History, Syntheses, and Biological Profile of the Greatest “Minor” Cannabinoid. Plants, 11(21), 2896. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants11212896
- Sholler, D. J., Zamarripa, C. A., Spindle, T. R., Martin, E. L., Kuntz, D., Vandrey, R., & Grabenauer, M. (2022). Urinary Excretion Profile of Cannabinoid Analytes Following Acute Administration of Oral and Vaporized Cannabis in Infrequent Cannabis Users. Journal of Analytical Toxicology, 46(8), 882–890. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkac042
- Somvanshi, R. K., Zou, S., Kadhim, S., Padania, S., Hsu, E., & Kumar, U. (2022). Cannabinol modulates neuroprotection and intraocular pressure: A potential multi-target therapeutic intervention for glaucoma. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Molecular Basis of Disease, 1868(3), 166325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166325
- Walsh, K. B., McKinney, A. E., & Holmes, A. E. (2021). Minor Cannabinoids: Biosynthesis, Molecular Pharmacology and Potential Therapeutic Uses. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 12, 777804. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.777804
- Tsagareli, M., Kvachadze, I., & Simone, D. (2021). ANTINOCICEPTIVE TOLERANCE TO CANNABINOIDS IN ADULT MALE MICE: A PILOT STUDY. Georgian Medical News, 148–153. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/357028527_ANTINOCICEPTIVE_TOLERANCE_TO_CANNABINOIDS_IN_ADULT_MALE_MICE_A_PILOT_STUDY
- Chousidis, I., Chatzimitakos, T., Leonardos, D., Filiou, M. D., Stalikas, C. D., & Leonardos, I. D. (2020). Cannabinol in the spotlight: Toxicometabolomic study and behavioral analysis of zebrafish embryos exposed to the unknown cannabinoid. Chemosphere, 252, 126417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126417
- Shahbazi, F., Grandi, V., Banerjee, A., & Trant, J. F. (2020). Cannabinoids and Cannabinoid Receptors: The Story so Far. iScience, 23(7). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101301
- Klahn, P. (2020). Cannabinoids-Promising Antimicrobial Drugs or Intoxicants with Benefits? Antibiotics, 9(6), 297. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9060297
- Cannabics Pharmaceuticals Inc. (2020, February 18). Cannabics Pharmaceuticals Study Shows Cannabinoids CBNA and CBCA Cause Necrosis Similarly to their Non-acidic Form. BioSpace. https://www.biospace.com/article/cannabics-pharmaceuticals-study-shows-cannabinoids-cbna-and-cbca-cause-necrosis-similarly-to-their-non-acidic-form/
- Wong, H., & Cairns, B. E. (2019). Cannabidiol, cannabinol and their combinations act as peripheral analgesics in a rat model of myofascial pain. Archives of Oral Biology, 104, 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.05.028
- Farrimond, J. A., Whalley, B. J., & Williams, C. M. (2012). Cannabinol and cannabidiol exert opposing effects on rat feeding patterns. Psychopharmacology, 223(1), 117–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2697-x
- Bastola, K. P., Hazekamp, A., & Verpoorte, R. (2007). Synthesis and Spectroscopic Characterization of Cannabinolic Acid. Planta Medica, 73(03), 273–275. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-967129
- United Nations. (1992, December 1). UNODC – Bulletin on Narcotics—1997 Issue 1—008. United Nations : Office on Drugs and Crime. //www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/bulletin/bulletin_1997-01-01_1_page008.html
- Karniol, I. G., Shirakawa, I., Takahashi, R. N., Knobel, E., & Musty, R. E. (1975). Effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol in man. Pharmacology, 13(6), 502–512. https://doi.org/10.1159/000136944
- Shoyama, Y., Yamauchi, T., & Nishioka, I. (1970). Cannabis. V. Cannabigerolic Acid Monomethyl Ether and Cannabinolic Acid. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 18(7), 1327–1332. https://doi.org/10.1248/cpb.18.1327
Editor’s note: This article was originally published on January 18, 2022, by Ali Mans Cornwell.

