You’d be forgiven for thinking that we know everything there is to know about cannabis. After all, as the most widely-used, often-illegal drug around, and with all the interest in its therapeutic properties, you’d expect scientists to already know basically everything about the plant. However, cannabidiphorol (CDBP) wasn’t discovered until late 2019, and despite some theoretical applications, scientists have barely started to scratch the surface of its potential.
So what is CBDP? How was it discovered? Is it legal? Here are the most important things to know about this rare cannabinoid.
What Is CBDP?
Cannabidiphorol (CBDP) is a cannabidiol (CBD)-like molecule that has a seven-carbon alkyl chain instead of the usual five.
Scientists have discovered over 150 cannabinoids in the plant, and CBDP – along with delta-9 THCP – is one of the most recent additions. The cannabinoid was discovered in 2019 by a group of Italian researchers, who were investigating the FM2 medical cannabis variety (one of the two allowed in Italy), particularly looking for cannabinoids with alkyl side-chains of different lengths.
In short, CBDP is identical to ordinary CBD, except it has a longer alkyl side-chain, seven carbon atoms long rather than five. The alkyl side-chain is a carbon-hydrogen chain with one less hydrogen atom than the standard “alkane” you might remember from organic chemistry. You can see the difference in the molecular structure easily if you know what you’re looking for, but the simple explanation is that CBDP is a slightly modified version of CBD, which also occurs naturally in cannabis plants.
What Does the Molecular Structure of CBDP Tell Us?
At present, we don’t know much about how the longer alkyl side-chain will impact the effects of CBDP relative to CBD. Unfortunately, the original researchers focused more on THCP in the study, but they are currently investigating CBDP’s potential for anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-epileptic activity.
The researchers point to the influence of the length of the alkyl side-chain – basically the long, jagged “tail”-like line you see on THC and CBD’s chemical structure – on the effects of THC on the body. Three carbon atoms is the minimum number to bind with the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. THC usually has five, and eight seems to be the peak for effective binding. The researchers discovered seven-carbon chain versions of THC and CBD, naming them THCP and CBDP.
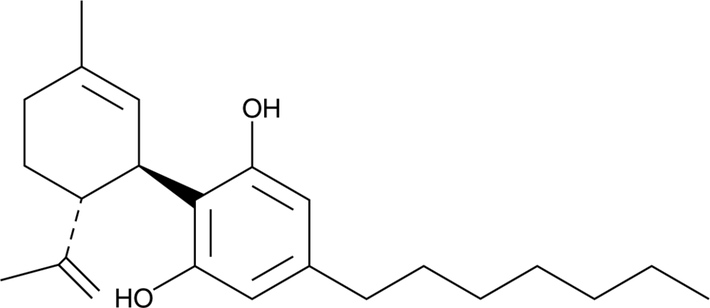
This is basically why THCP took most of the attention, even though CBDP was discovered at the same time – stronger THC could mean increased medicinal effectiveness, a stronger high, or equal effects at significantly lower doses, but what does a long alkyl-chain CBD molecule achieve? The authors themselves write:
“It is known that CBD binds with poor affinity to both CB1 and CB2 receptors. Therefore, the evaluation of the cannabimimetic activity of CBDP does not appear to be a high priority, although science can hold great surprises.”
This is basically “science” for “it doesn’t seem like it would make much difference to CBD’s effect, but who knows?”
What Are the Effects of CBDP?

The effects of CBDP are not precisely known at the moment. However, user reviews suggest – a little unreliably – that it is indeed like a stronger version of CBD.
The scientists who discovered CBDP didn’t test its effects, instead focusing on THCP. They found that THCP binds to receptors 33 times more strongly than regular THC, and many people have assumed this will carry over to CBDP too. However, as the authors point out, CBD’s binding affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors is pretty low, so it’s unclear whether the longer alkyl chain would actually make a difference.
There is more to the endocannabinoid system than just these receptors, though. CBD is known to inhibit FAAH (fatty acid amide hydrolase), which has the effect of boosting the body’s natural endocannabinoids, and it blocks pain through its effects at the TRP receptors. For CBDP, these are also areas where further research could reveal additional benefits, but again, there isn’t any hard evidence on this yet.
User reviews are arguably the best source of information on the subjective effects, but at present there are many issues with these. One example is a positive CBDP review, but a little digging shows that the product contained 3.5% THCP, which is known to be stronger than regular THC. The question – as it is with the other reviews we found during research – is which cannabinoid is really affecting you here?
So the unfortunate reality is that nobody knows what the effects of CBDP are. We can assume it will be like CBD, but the basis for this is paper-thin, given that the longer alkyl chain probably won’t be as relevant as it is with THC. The reviews we found do say it’s like a stronger version of CBD, but there seems to be very little knowledge of the effects of pure CBDP.
Potential Uses for CBDP
The potential uses for CBDP are very unclear at the moment, although early evidence suggests it will behave similarly to CBD. In particular, preclinical research shows that CBDP reduces the viability of cancer cells much like CBD, and it is being investigated for anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-epileptic activity.
The challenge with working out potential uses for CBDP is that very few studies are available at the moment – there are just three hits on PubMed, for instance – and assumptions about what it does aren’t as valid as they may seem. While a longer alkyl chain appears to improve binding to the CB receptors, CBD has a pretty low affinity for these anyway and the overall picture is pretty complicated. It’s certainly possible that it will turn out to work like some kind of “super CBD,” but it’s also possible that the longer alkyl chain will produce other, harder-to-predict effects.
One of the only pieces of research on CBDP looked at its effect on breast cancer cell lines with CB receptors. The in-vitro study found that CBDP reduced cell viability and induced oxidative stress in a manner similar to ordinary CBD. This doesn’t mean it will treat cancer effectively in living humans – after all, even a handgun kills cancer in a petri dish – but it is a sign that some of the effects of CBD may be expected from CBDP too.
The researchers who discovered CBDP note that they are currently investigating its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-epileptic properties, in line with the benefits of CBD. While this work is still ongoing and we can’t really know anything until it is, this is an important sign of what researchers expect in terms of benefits.
However, other than that, there is no solid evidence to base any recommendations on. If it works like CBD – which is not guaranteed – then we can expect it to help with pain, anxiety, depression, seizure disorders and more. These potential uses will need to be confirmed by research, though.
One of the discoverers of CBDP, Giuseppe Cannazza, commented to Cannabis Science and Technology that:
“No pharmacokinetic test was performed on CBDP and THCP. We can only speculate that they are more lipophilic molecules than the respective CBD and THC and therefore they could cross the blood-brain barrier more easily by passive diffusion. However, the road is still long for a clear understanding of their biological activity.”
Risks of CBDP
Just like we can’t be sure of the benefits of CBDP, we can’t be hugely sure of the risks either. However, it’s hypothesized that it may have a mild risk profile much like CBD.
Some sources imply that CBDP will be safe provided that the company who extracts it does their due diligence and avoids contamination. While there is no reason to assume that there will be a risk from CBDP – again, treating CBD itself as a rough guide – there really isn’t very much to base any type of answer on. Until we have the basic knowledge as to how exactly CBDP interacts with the body or even user reports in the form of a survey, it’s very difficult to predict.
It is certainly true that as with CBD products, ensuring the product you get is high quality is an important step in making sure it’s safe. As always, you should only choose products from a reputable vendor with a Certificate of Analysis (COA) available, ideally showing that it’s free from pesticides, microbes and other contaminants like heavy metals.
However, provided that you do this, there’s no need to be alarmist about the risks. It’s likely that – as with most cannabinoids – any risks that exist are fairly minor. But it’s important to note that we don’t really know right now.
That said, the main side effects of CBD may be a good guide to what to expect from CBDP:
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Drowsiness/sleepiness
- Loss of appetite
Again though, keep in mind that we don’t actually know whether these side effects will happen with CBDP products. It’s just an educated guess.
What Is the Right Dose of CBDP to Take?
Nobody knows what dose of CBDP you should take, although the assumption is that this should be lower than the dose you would take of a typical CBD product.
The promise of CBDP is that – as was demonstrated for THCP – it will produce effects at lower doses because it binds to receptors more efficiently. However, this has not been tested and any user reports we’ve been able to locate have been too vague to turn into a recommendation. If you have CBDP, the best advice is to take a much lower dose than you would take of CBD and judge the effects from there.
Is CBDP Legal?
CBDP would be legal in the US if it was obtained from hemp or if it came from marijuana in a state with either medical or recreational legalization.
CBDP was originally identified in the FM2 strain of cannabis, which is a high-CBD strain used for medical purposes in Italy. This strain has a higher THC content than would be permitted as “hemp” in the US, however, it’s possible that this compound could either be found in hemp or derived from hemp components. In this case, it would be legal in the US provided the delta-9 THC level remained below 0.3%.
Where Can You Buy CBDP? What Should You Look For?
Unfortunately, there aren’t many commercial sources for CBDP at the moment, but some stores do carry products and you can also buy from chemical companies.
CBDP products are hard to find because the cannabinoid is pretty rare and so extraction is expensive. This means that available options – such as this – tend to have much lower levels of CBDP combined with higher levels of CBD or something similar. Aside from that, companies like Cayman Chemical sell solutions containing CBDP, although it is very expensive and not suitable for general consumer use.
However, if you are going to be buying a CBDP product, you should follow the general guidelines you would when buying any hemp, CBD or cannabis product. In particular:
- Check for a COA: The most important thing you can do when buying any CBDP product is check the Certificate of Analysis (COA). Notably, you should look at the actual quantity of CBDP, mainly to check that there’s enough of it to justify the purchase (one example product contains about 1 mg/mL of CBDP, and about 50 times as much CBD). If the product doesn’t have a COA, don’t buy it.
- Consider competing cannabinoids: Some of the Reddit reviews of CBDP are hard to interpret because the product also contained substantial amounts of THCP, and this is one thing to look out for. If there are larger amounts of other cannabinoids, while CBDP will still likely have an effect, it will be difficult to tell where exactly the effect comes from. This isn’t necessarily bad – you might like the combination – but it makes it hard to know if the CBDP is really doing anything.
- Choose reputable companies: As always, it’s better to buy from a store where you can see user reviews and ideally find other information online. If a site like ours has reviewed the product and others from the company, it’s probably a safe choice unless the review says otherwise.
Conclusion
CBDP is an exciting, newly-discovered cannabinoid, but it’s hard to ignore the large cloud of uncertainty hanging over everything about the molecule. With more interest in its psychoactive cousin THCP, we have only bare-bones information about the cannabinoid and what it may do. This makes it a great choice for future research into cannabinoids, but a fairly uncertain bet from a consumer perspective.
In other words, it might be the super-CBD we were expecting, but it still could be a total dud.
References
- de Almeida, D. L., & Devi, L. A. (2020). Diversity of molecular targets and signaling pathways for CBD. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives, 8(6). https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.682
- Citti, C., Linciano, P., Russo, F., Luongo, L., Iannotta, M., Maione, S., Laganà, A., Capriotti, A. L., Forni, F., Vandelli, M. A., Gigli, G., & Cannazza, G. (2019). A novel phytocannabinoid isolated from Cannabis Sativa L. with an in vivo cannabimimetic activity higher than Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol: Δ9-tetrahydrocannabiphorol. Scientific Reports, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-56785-1
- Muller, C., Morales, P., & Reggio, P. H. (2019). Cannabinoid ligands targeting TRP channels. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2018.00487
- Pertwee, R. G. (2008). The diverse CB1 and CB2 receptor pharmacology of three plant cannabinoids: Δ9‐tetrahydrocannabinol, cannabidiol and Δ9‐tetrahydrocannabivarin. British Journal of Pharmacology, 153(2), 199–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjp.0707442
- Poli, P., Salvadori, C., & Sannino, C. (2018). Comparison between Cannabis Flos and Cannabis FM2 effects on Chronic Neuropatic Pain . Pathos, 25(1), 8–14. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.30458/PA2018-183
- Salbini, M., Quarta, A., Russo, F., Giudetti, A. M., Citti, C., Cannazza, G., Gigli, G., Vergara, D., & Gaballo, A. (2021). Oxidative stress and multi-organel damage induced by two novel phytocannabinoids, CBDB and CBDP, in breast cancer cells. Molecules, 26(18), 5576. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26185576
- Shahbazi, F., Grandi, V., Banerjee, A., & Trant, J. F. (2020). Cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors: The story so far. iScience, 23(7), 101301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101301
- Souza, J. D., Pacheco, J. C., Rossi, G. N., de-Paulo, B. O., Zuardi, A. W., Guimarães, F. S., Hallak, J. E., Crippa, J. A., & Dos Santos, R. G. (2022). Adverse effects of oral cannabidiol: An updated systematic review of randomized controlled trials (2020–2022). Pharmaceutics, 14(12), 2598. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics14122598
Last medically reviewed on August 10, 2023.
